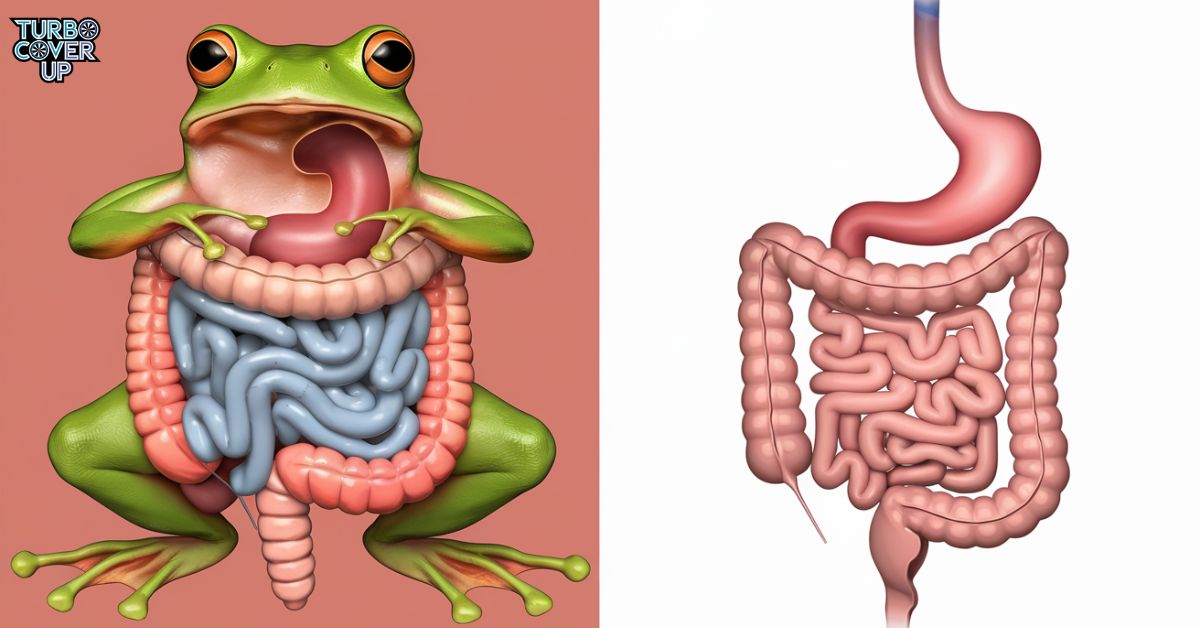
The frog digestive system refers to the organs that process food in frogs. It is simpler than the human digestive system. Frogs have unique adaptations, like a sticky tongue for catching prey.
The human digestive system is more complex and involves several organs working together. It includes specialized accessory organs that aid in digestion. Both systems aim to convert food into energy and nutrients, but they do so differently.
Digestive Differences
The digestive differences between humans and frogs are quite interesting. Humans have a complex digestive system with many parts. Food enters through the mouth and travels down the esophagus to the stomach.
Here, it mixes with acids and enzymes. Then, food moves to the small intestine, where most digestion and absorption happen. The large intestine takes care of waste before it leaves the body.
Frogs have a simpler digestive system. They also eat through their mouths, but their teeth are not strong. Instead, frogs use their sticky tongues to catch food quickly. After catching food, it travels down the esophagus to the stomach.
Most digestion occurs in the small intestine, just like in humans. However, frogs have a cloaca. This part helps them remove both liquid and solid waste from their bodies at the same time.
The main difference is in how these systems function. Humans need their complex system for a varied diet. Frogs eat mostly insects, so their system is adapted for this type of food.
Both systems convert food into energy and nutrients, but they do so in ways that suit their needs. Understanding these differences shows how animals adapt to their environments.
Human and Frog Respiratory System
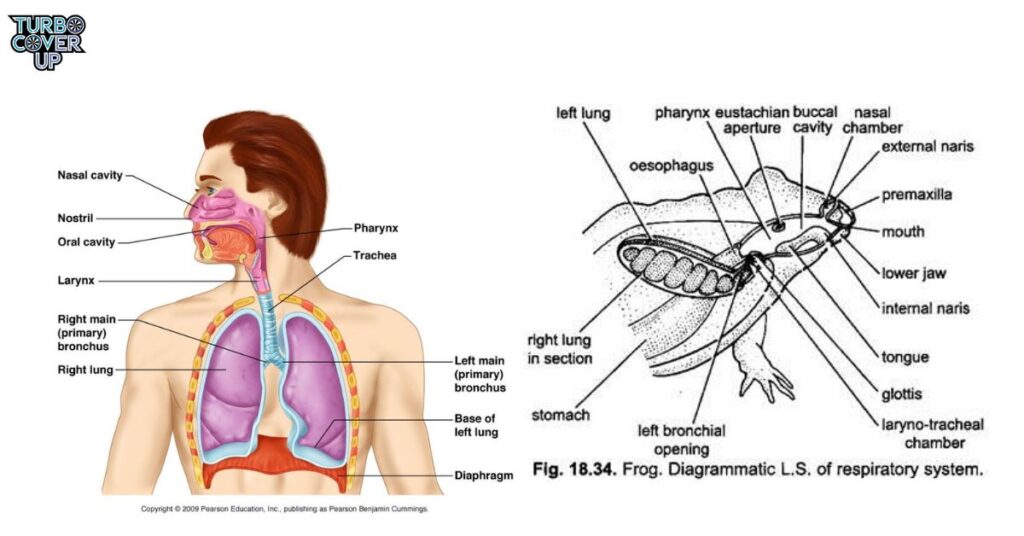
The human respiratory system helps us breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Our lungs play a crucial role in this process. When we inhale, fresh air fills our lungs. Our heart then pumps oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the body. This oxygen is essential for our cells to function well.
Frogs have a different way of breathing. They also have lungs, but they do not have a diaphragm. Frogs breathe in through their nostrils and fill skin sacs in their throats with air.
Muscles in their mouths then push the air into their lungs. This process helps frogs get oxygen, but they can also breathe through their skin. This special ability allows them to absorb oxygen directly from water.
Both humans and frogs need oxygen to survive. Their respiratory systems accomplish this task but in unique ways. Humans rely mainly on their lungs for breathing. Frogs use both their lungs and skin.
These differences show how animals adapt to their environments. Understanding these systems helps us appreciate the amazing ways life functions on Earth.
Respiratory Differences of Frog and Human
The respiratory differences between frogs and humans are interesting. Frogs breathe through their skin and lungs. This process is called cutaneous respiration. Frogs need moisture on their skin to absorb oxygen from the air or water. This adaptation helps frogs survive in wet environments.
In contrast, humans only breathe through their lungs. They use a muscle called the diaphragm to pull air into their lungs. When humans inhale, oxygen enters the lungs and moves into the blood.
This oxygen-rich blood then travels throughout the body to provide energy. Humans exhale carbon dioxide, which is a waste product of using oxygen.
Frogs have a unique way of inhaling. They fill special sacs in their throats with air. By pushing down their mouths, they force the air into their lungs. Humans do not have this ability. They can breathe through both their noses and mouths, which gives them more options.
Overall, while both systems help animals breathe, they function in different ways. Understanding these differences shows how frogs and humans adapt to their environments
Human and Frog Circulatory System
The circulatory system is important for both humans and frogs. This system includes the heart and blood vessels. The heart pumps blood, which carries oxygen and nutrients to all body parts. In humans, the heart has four chambers. This structure helps keep oxygen-rich blood separate from oxygen-poor blood.
Frogs have a simpler heart with only three chambers. This heart mixes oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood. While this makes their circulatory system less efficient, frogs can breathe through their skin.
This ability reduces the need for a more complex system. Frogs use lungs and skin to take in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide.
Blood vessels in both animals are similar. Humans have arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Veins return blood to the heart. Frogs have the same types of blood vessels, but their heart structure changes how blood flows. Both systems aim to deliver oxygen and nutrients. They also help remove waste products. Understanding these systems helps us appreciate how different animals adapt to their environments.
Circulatory Differences of Frog and Human
The circulatory system is vital for all animals. In humans, it consists of a four-chambered heart. This structure keeps oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood separate. Blood travels through arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins bring blood back. The heart works hard to pump blood throughout the body.
Frogs have a different structure. They possess a three-chambered heart. This heart mixes oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood. The mixed blood flows through their body, which is less efficient than the human system.
Frogs have to rely on cutaneous respiration, which means they can breathe through their skin. This adaptation helps them get enough oxygen from their surroundings.
The circulatory differences between frogs and humans show how each species meets its needs. While humans need a more efficient system, frogs can survive with their simpler heart.
Their environment allows frogs to breathe in different ways. Understanding these differences helps us appreciate how nature works. Each animal has a unique way of surviving and thriving in its habitat.
Human and Frog Muscular System
The human muscular system consists of three types of muscles: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscles attach to bones and allow movement. These muscles work when you want to walk, run, or play.
Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart and works automatically to pump blood. Smooth muscles are in organs like the stomach and help with digestion.
Frogs also have a muscular system with similar types of muscles. They use skeletal muscles for movement, just like humans. Frogs can jump high and swim fast because of strong leg muscles.
Their smooth muscles help digest food and move it through the digestive system. Unlike humans, frogs have unique muscles that help them catch prey with their tongues. Frogs have a sticky tongue that snaps out quickly.
Both humans and frogs rely on their muscular systems for daily activities. While humans use muscles to perform various tasks, frogs focus on jumping and catching food. The design of their muscles helps them thrive in their environments. Understanding these differences shows how nature adapts creatures to their surroundings.
Muscular Similarities/Differences
| Aspect | Humans | Frogs |
| Muscle Types | Humans have skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. | Frogs also have skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. |
| Movement | Humans use muscles to walk, run, and jump. | Frogs use muscles to hop and swim. |
| Muscle Control | Humans can control their muscles voluntarily. | Frogs can control most muscles, but some work automatically. |
| Muscle Strength | Human muscles can be very strong for lifting weights. | Frog muscles are strong for jumping far distances. |
| Muscle Size | Human muscles can vary in size based on exercise. | Frog muscles are smaller but very powerful for quick movements. |
| Muscle Location | Human muscles are attached to bones throughout the body. | Frog muscles attach to bones in the limbs and back. |
| Muscle Fiber | Human muscles have different types of fibers for endurance and strength. | Frog muscles also have different fibers but focus on quick bursts of power. |
Human and Frog Nervous System
The human and frog nervous system controls how bodies react to their surroundings. Both systems help animals sense things like sounds, light, and touch. The nervous system sends signals between the brain and the rest of the body. In humans, the brain is larger and more complex. It allows for advanced thinking and problem-solving.
Frogs also have a nervous system, but it works a bit differently. Their brains are smaller and simpler than those of humans. This difference affects how frogs respond to their environment.
Frogs rely more on instinct than learned behavior. For example, they jump when they see movement, showing quick reactions. The frog’s nervous system allows it to react swiftly to danger, which helps it survive.
Both systems include nerves that connect to different body parts. In frogs, the nervous system helps with basic functions like swimming and catching food. Humans, however, use their systems for complex tasks, like talking and writing. Despite their differences, the human and frog nervous system both play essential roles in helping these animals interact with their world.
Nervous Similarities/Differences
| Feature | Humans | Frogs |
| Structure | Humans have a complex nervous system. | Frogs have a simpler nervous system. |
| Brain Size | The human brain is large and advanced. | Frogs have a smaller brain with basic functions. |
| Spinal Cord | Humans have a long spinal cord with many nerves. | Frogs have a shorter spinal cord. |
| Sensory Organs | Humans use five main senses: sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell. | Frogs also have five senses but rely more on sight and hearing. |
| Response Time | Humans respond quickly to danger. | Frogs also respond quickly but in a different way. |
| Movement Control | Humans have precise control over movement. | Frogs have strong reflexes for jumping and swimming. |
| Nerve Pathways | Humans have complex nerve pathways for communication. | Frogs have simpler pathways for faster reactions. |
| Adaptation | Humans adapt through learning and experience. | Frogs adapt through instinct and reflexes. |
Human and Frog Skeletal System
The human skeletal system supports the body and protects internal organs. It is made up of bones, which give structure and shape. Humans have 206 bones that work together to allow movement. These bones connect at joints. Muscles pull on bones to create movement.
The frog skeletal system is different but has some similarities. Frogs have bones too, and they also provide support. They have fewer bones than humans, about 200 in total. Frogs have long legs that help them jump. Their bones allow them to swim well. Frogs do not have necks like humans, so they cannot turn their heads.
Both skeletal systems help with movement and protection. In humans, bones are strong and flexible, allowing for various activities. Frogs have adapted bones that support their jumping and swimming skills. Their bones are lighter, which helps them move quickly. Understanding these differences shows how each system fits the needs of the animal. Studying the human and frog skeletal system reveals how living things adapt to their environments.
Skeletal Similarities/Differences
| Aspect | Frogs | Humans |
| Skeleton Type | Frogs have a skeleton made of bones. | Humans also have a skeleton made of bones. |
| Limbs | Frogs have four limbs. | Humans have two arms and two legs. |
| Humerus | Frogs have a humerus in their front legs. | Humans have a humerus in their arms. |
| Radius and Ulna | Frogs’ radius and ulna are fused together. | Humans have separate radius and ulna bones. |
| Leg Bones | Frogs have a femur in their back legs. | Humans also have a femur in their legs. |
| Pelvis | Frogs have a flexible pelvis for jumping. | Humans have a strong pelvis for walking. |
| Neck | Frogs do not have necks. | Humans have a neck that moves easily. |
| Ribs | Frogs lack true ribs. | Humans have a rib cage for protection. |
| Digits | Frogs have five toes on back legs. | Humans have five fingers on each hand. |
| Skull Structure | Frogs have a simple skull shape. | Humans have a more complex skull structure. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the similarities between the frog and human digestive system?
Both systems break down food for energy and nutrients. Frogs and humans use similar organs like the stomach and intestines.
What are the differences between frogs and humans?
Frogs breathe through their skin and have a simpler heart. Humans have more complex respiratory and circulatory systems.
How does the frog’s circulatory system differ from humans?
Frogs have a three-chambered heart, while humans have four chambers for better oxygen separation.
Which organs do humans have that frogs do not?
Humans have a diaphragm and a true rib cage, while frogs lack these structures.
What are 3 differences between frog and human anatomy?
Humans walk upright, have separate radius and ulna bones, and have necks. Frogs have fused limb bones and no neck.
How is the respiratory system of frogs and humans similar?
Both use lungs to exchange gases. However, frogs also use their skin for breathing.
What are the similarities between frogs and humans?
Both species share similar organs like the liver, stomach, and heart.
Conclusion
The Frog Digestive System vs. Human shows us how animals have different ways of processing food. Both systems break down food into nutrients the body needs. Frogs use their sticky tongue to catch food, and humans chew food with their teeth. Frogs do most digestion in their small intestine, while humans use more complex organs like the stomach and pancreas.
Even though there are differences, frogs and humans share some digestive parts. Both have a stomach, intestines, and a liver that helps with digestion. However, frogs have a cloaca to remove waste, while humans use the rectum. Learning about the Frog Digestive System vs. Human helps us understand how both species survive in their environments.
>>>Read more: